Understanding CPM in Digital Advertising

Using digital marketing is essential for reaching consumers and increasing awareness. In digital marketing, cost per mile, or CPM, is a common pricing formula that shows how much a marketer must pay for each thousand impressions of a digital ad.
We will explain what CPM is, why it matters, and how to calculate it in this comprehensive guide.
What Is CPM?
In digital marketing, CPM stands for the average cost of one thousand ad impressions. It is computed by multiplying by 1000 after dividing the cost by the number of impressions.
CPM, which is based on how many times an ad is loaded and viewed as part of a web page, is used for campaigns that aim to reach thousands of people. Comprehending cost-per-click (CPM) is essential for digital marketing strategies and their integration into larger firm marketing campaigns.
How Does CPM Work?
Companies charge for ad views using the typical internet marketing metric known as CPM. It is frequently utilized in online advertising, web traffic marketing, and media selection. CPM pricing is used by platforms such as Facebook campaigns and Google Ads.
Unlike a cost per click (CPC) model, which measures low awareness of a firm, a cost per thousand (CPM) model assesses high awareness of a brand because one impression has minimal weight.
How To Calculate CPM?
The entire cost of the advertising campaign divided by the total number of impressions yields the CPM (Cost Per Mille), which is then multiplied by 1000. The equation is:
CPM is equal to (Total Impressions / Total Cost) * 1000.
The CPM would be determined as follows, for instance, if an advertiser spent $500 on a campaign that resulted in 100,000 impressions:
$5 is the CPM, or ($500 / 100,000) * 1000.
Accordingly, the advertiser would pay $5 for each thousand impressions of their advertisement, or a $5 CPM for this campaign.
CTR and CPM
The metric known as click-through rate, or CTR, counts the number of clicks an advertisement gets from its online impressions. The number of clicks divided by the total number of impressions and multiplied by 100 is the formula for CTR.
CTR is a metric used to assess how successful a marketing effort is. It can offer information on whether a CPM marketing effort is worthwhile, enabling companies to improve their tactics and get superior outcomes.
In light of this, it’s important to remember that there are numerous more price options for digital advertisements outside CPM.
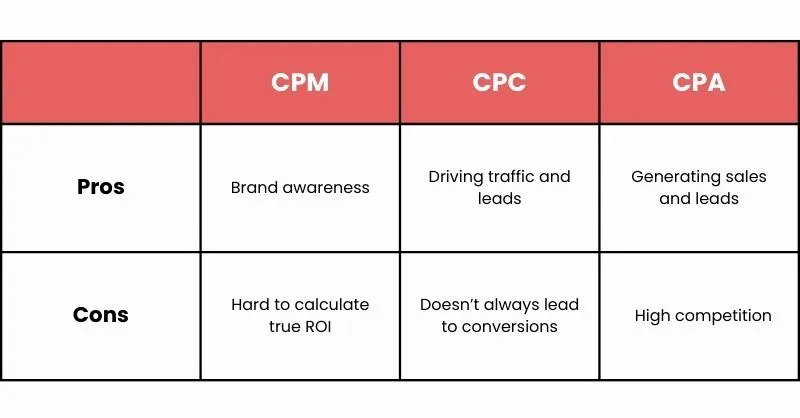
CPM vs. CPC vs. CPA
In addition to cost per click (CPD) and cost per impression (CPM), there is cost per action (CPA). Depending on the marketing objectives, each of the three has pros and cons. As was previously said, CPM is a conventional internet marketing indicator for ad view pricing.
Another common price strategy in digital marketing is CPC, or cost per click. With CPC, advertisers only pay when someone clicks on their advertisement, as opposed to just seeing it as with CPM. This technique works well for efforts that try to increase website traffic or lead generation.
However, CPA takes a step further by only charging advertisers in response to particular actions, such a purchase or the submission of a lead form. Because CPA guarantees that advertisers only pay for outcomes, it is advantageous for campaigns that intend to create leads or sales. In affiliate marketing, where publishers receive a fee from advertisers for each sale or lead they produce, this pricing model is frequently utilized.
Tips for Getting Started With CPM Campaigns
Starting CPM campaigns can be a great approach for companies to reach a large audience with their advertisements. For individuals who are unfamiliar with CPM marketing, it can be difficult to know where to begin. The following advice can assist companies in launching CPM campaigns:
1. Establish Campaign Objectives
Businesses should identify their objectives, such as raising brand awareness or increasing website traffic, before launching a CPM campaign. Businesses may produce more effective targeted marketing and campaigns by having clear goals.
2. Determine Who Your Target Market Is
Although understanding your target market is vital for any advertising campaign, CPM ads require it even more since companies are paying for each impression. Advertising that is more relevant to the target audience can be produced by businesses by identifying the target population based on their demographics, interests, or behaviors
3. Select the Appropriate Ad Format
There are numerous ad formats at one’s disposal, such as native ads, video commercials, and banner ads. Every format has advantages and disadvantages, so companies should select the best one for their objectives and target market.
4. Establish a Fair Budget
Because CPM campaigns can be costly, companies should establish a budget that is both acceptable and in line with their objectives. Monitoring and making necessary adjustments to the budget is also crucial.
5. Evaluate and Enhance Ads
For CPM campaigns to be as effective as possible, testing and tweaking are necessary. To determine what works best, businesses should test a variety of ad styles, targeting options, and content. Businesses can maximize the benefits of their CPM campaigns by implementing ongoing optimization based on the data.
6. Track the effectiveness of campaigns
A CPM campaign’s performance must be tracked to make sure its objectives are met. Companies should monitor campaign performance data, such as conversions and CTR, and make necessary adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cost per mille, or CPM for short, is the price an advertiser must pay for every thousand ad impressions.
The overall cost of the advertising campaign divided by the total number of impressions yields the CPM, which is then multiplied by 1000.
Advertisers can effectively budget and gauge the success of their advertising campaigns by counting the number of impressions they create thanks to an understanding of CPM.
Disclaimer: Above all information is for general reference only and sourced from internet, before making any kind of decision please visit the authorized websites of authorities and service providers.

